Blogs category
Featured Blogs

High-Gloss Polishing for 6xxx Series – The Mirror of Industrial Design
.

Raindrop Diamond Textures – Fluidity in Rigid Metal
.

The "Sandblast + Bright Matte" Hybrid – Orchestrating Tactile Contrast
.
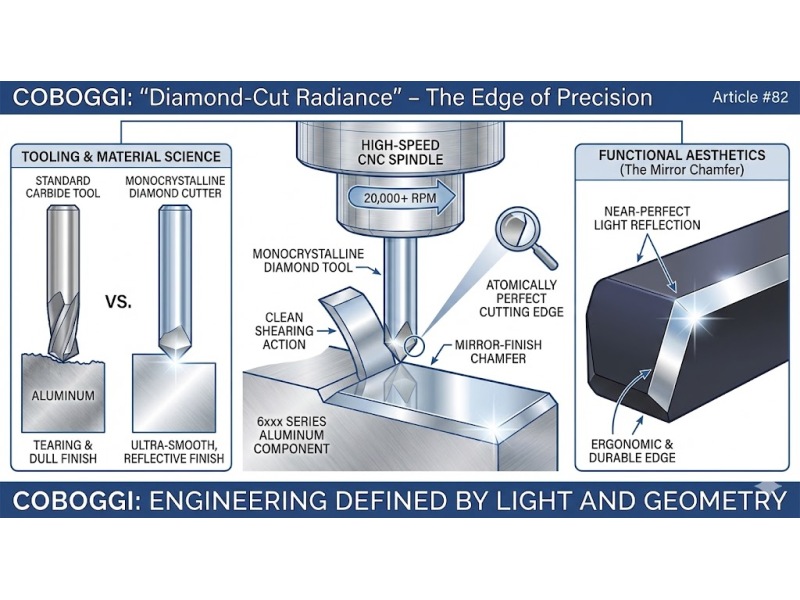
Diamond-Cut Radiance – The Edge of Precision
.
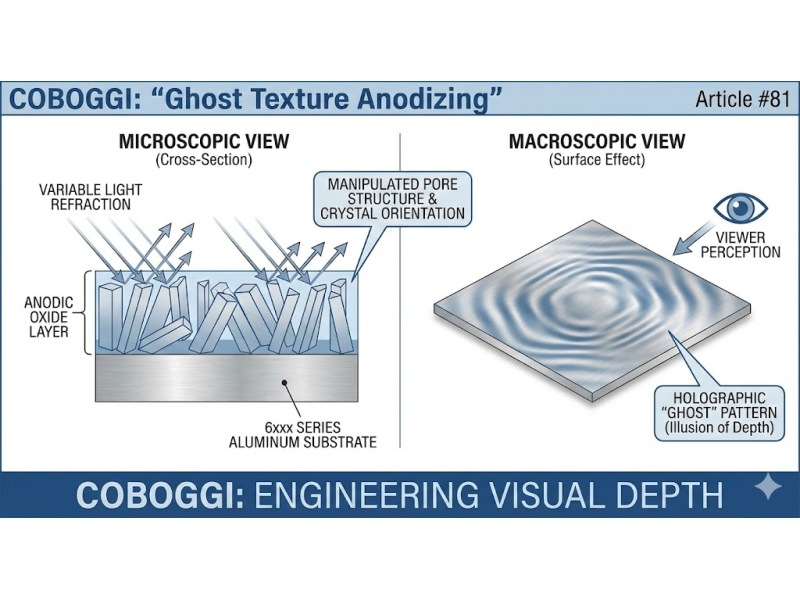
The Ghost Texture Anodizing – Engineering Visual Depth
.
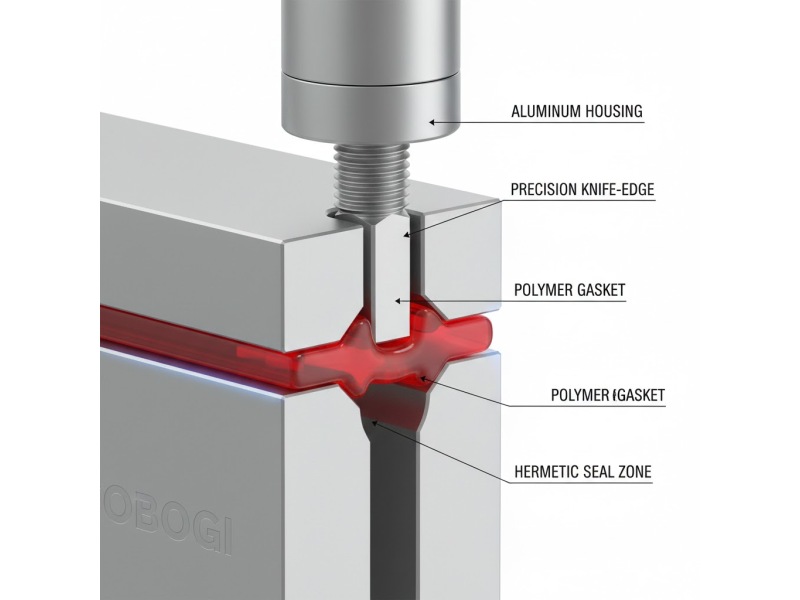
The Precision of Seams – Vacuum-Tight Aluminum Joining
.













 English
English German
German French
French Russian
Russian Spanish
Spanish Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Khmer
Khmer Portuguese
Portuguese Ukrainian
Ukrainian Arabic
Arabic Italian
Italian Afrikaans
Afrikaans Albanian
Albanian Armenian
Armenian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Basque
Basque Belarusian
Belarusian Bulgarian
Bulgarian Catalan
Catalan Croatian
Croatian Czech
Czech Danish
Danish Dutch
Dutch Estonian
Estonian Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Galician
Galician Georgian
Georgian Greek
Greek Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Hungarian
Hungarian Icelandic
Icelandic Indonesian
Indonesian Irish
Irish Latvian
Latvian Lithuanian
Lithuanian Macedonian
Macedonian Malay
Malay Maltese
Maltese Norwegian
Norwegian Persian
Persian Polish
Polish Romanian
Romanian Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Swedish
Swedish Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Urdu
Urdu Vietnamese
Vietnamese Welsh
Welsh Yiddish
Yiddish